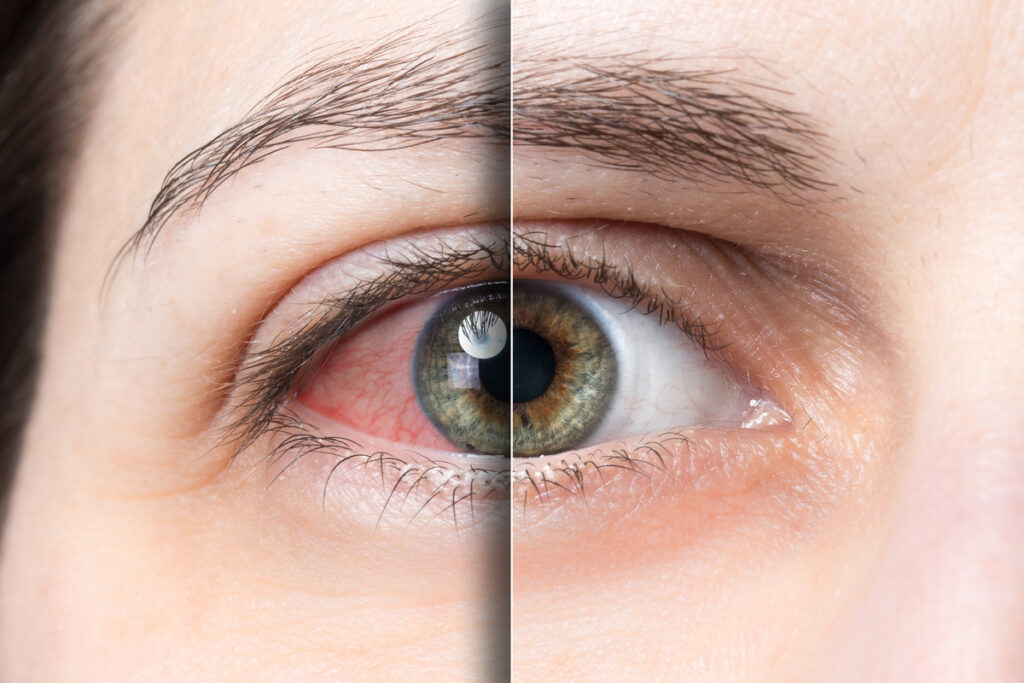
What Every Patient Should Know About Glaucoma Symptoms and Treatment
Glaucoma is a complex eye condition that significantly impacts vision and overall eye health. As one of the leading causes of blindness globally, it is vital for patients to understand its symptoms, the importance of early detection, and available treatment options. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of glaucoma, its symptoms, and approaches to treatment, and how one can live with this condition effectively.
Understanding Glaucoma: An Overview
The Basics of Glaucoma
Glaucoma is primarily characterized by damage to the optic nerve, often associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). The condition can lead to irreversible vision loss if not diagnosed and managed promptly. Glaucoma treatment is usually categorized into two main types: open-angle and angle-closure glaucoma. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for recognizing the condition early.
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common type, where the drainage canals become clogged over time, resulting in gradual pressure build-up. Angle-closure glaucoma, on the other hand, occurs when the iris bulges forward, blocking the drainage angle and causing a sudden rise in eye pressure, which can require immediate medical attention. Symptoms of angle-closure glaucoma may include severe eye pain, headache, nausea, and blurred vision, making it a medical emergency that necessitates swift intervention to prevent lasting damage to vision.
Types of Glaucoma
In addition to open-angle and angle-closure glaucoma, there are several other less common types worth noting:
Normal-tension glaucoma: where optic nerve damage occurs despite normal eye pressure.
Secondary glaucoma: resulting from another medical condition, such as diabetes or inflammation.
Pediatric glaucoma: a rare form affecting infants and children, which often requires early intervention.
Each type of glaucoma can progress differently and may require tailored treatment plans, making it crucial for patients to be aware of their specific diagnosis. For instance, normal-tension glaucoma often presents a unique challenge for healthcare providers, as standard pressure-lowering treatments may not be effective. This necessitates a more comprehensive approach that includes monitoring and possibly neuroprotective strategies to safeguard the optic nerve. Similarly, pediatric glaucoma can be particularly complex due to the developmental considerations involved, often requiring a multidisciplinary team to address both the medical and psychological needs of young patients.
Furthermore, the risk factors for glaucoma extend beyond intraocular pressure. Age, family history, and certain medical conditions can significantly increase an individual's likelihood of developing the disease. Regular eye examinations are vital, especially for those in high-risk categories, as early detection can lead to more effective management strategies. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, may also play a role in reducing the risk of glaucoma, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to eye health.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Glaucoma
Early Warning Signs
Glaucoma is often referred to as the "silent thief of sight" because it may not present noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, some warning signs may indicate the onset of the disease:
Gradual loss of peripheral vision.
Difficulty adjusting to darkness.
Seeing halos around lights.
Recognizing these early warning signs is essential, as they can prompt timely examinations and interventions from eye care professionals. Regular eye check-ups become crucial, especially for individuals over the age of 40 or those with a family history of glaucoma. Eye care specialists often recommend comprehensive eye exams that include measuring intraocular pressure and assessing the optic nerve's health, which can help in early detection. Read more about Glaucoma at https://health.ucdavis.edu/conditions/glaucoma
Progression of Symptoms
As glaucoma advances, patients may experience more severe symptoms that can significantly affect their daily lives. These can include:
Blind spots in the central or peripheral vision.
Severe eye pain.
Nausea or vomiting.
If any of these symptoms are experienced, especially in conjunction with sudden vision changes, immediate medical attention should be sought. The progression of glaucoma can vary widely among individuals, and while some may experience a slow decline in vision, others may face rapid deterioration. Understanding the different types of glaucoma, such as open-angle and angle-closure glaucoma, is also vital, as they can manifest distinct symptoms and require different treatment approaches. For instance, angle-closure glaucoma may present with acute symptoms like intense headache and blurred vision, necessitating urgent care to prevent irreversible damage.
The Importance of Early Detection
Regular Eye Exams and Glaucoma
Early detection of glaucoma can greatly affect the prognosis. Regular eye exams are essential as they can help identify elevated IOP and other changes in the optic nerve before significant damage occurs. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends that:
Adults aged 40 and older should have a comprehensive eye examination every 2 to 4 years.
Higher risk individuals, such as those with a family history of glaucoma, should have examinations more frequently.
Through routine exams, the likelihood of detecting glaucoma early increases, providing more options for effective treatment. Additionally, advancements in technology have made it possible for eye care professionals to utilize tools such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and visual field testing to gain a more detailed understanding of the optic nerve's health. These diagnostic methods not only enhance the accuracy of glaucoma detection but also allow for ongoing monitoring of any changes over time, which is crucial for managing the disease effectively.
Risk Factors for Glaucoma
Various risk factors can elevate the chances of developing glaucoma, including:
Age: The risk increases as individuals age, particularly after 60.
Family history: Genetic predisposition can play a significant role.
Medical history: Conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure may elevate risks.
Understanding these factors can aid patients in recognizing potential risks for themselves and encourage proactive medical consultations. Moreover, lifestyle choices such as diet, exercise, and smoking can also influence the likelihood of developing glaucoma. For instance, a diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may contribute to better eye health, while regular physical activity can help maintain healthy intraocular pressure. By being informed about these risk factors and making conscious lifestyle adjustments, individuals can take significant steps toward preserving their vision and overall eye health.
Treatment Options for Glaucoma
Medications for Glaucoma
Treatment for glaucoma primarily aims to reduce intraocular pressure and prevent damage to the optic nerve. Medications typically include:
Prostaglandin analogs: to increase fluid drainage from the eye.
Beta-blockers: to decrease fluid production in the eye.
Alpha agonists: which work similarly to beta-blockers but also improve drainage.
These medications may be prescribed individually or in combination to achieve optimal IOP control. It's important for patients to adhere to their prescribed regimen, as inconsistent use can lead to fluctuations in intraocular pressure, potentially exacerbating the condition. Regular follow-ups with an eye care professional are crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and make necessary adjustments. Additionally, some patients may experience side effects from these medications, such as eye redness or changes in eyelash growth, which should be discussed with their healthcare provider.
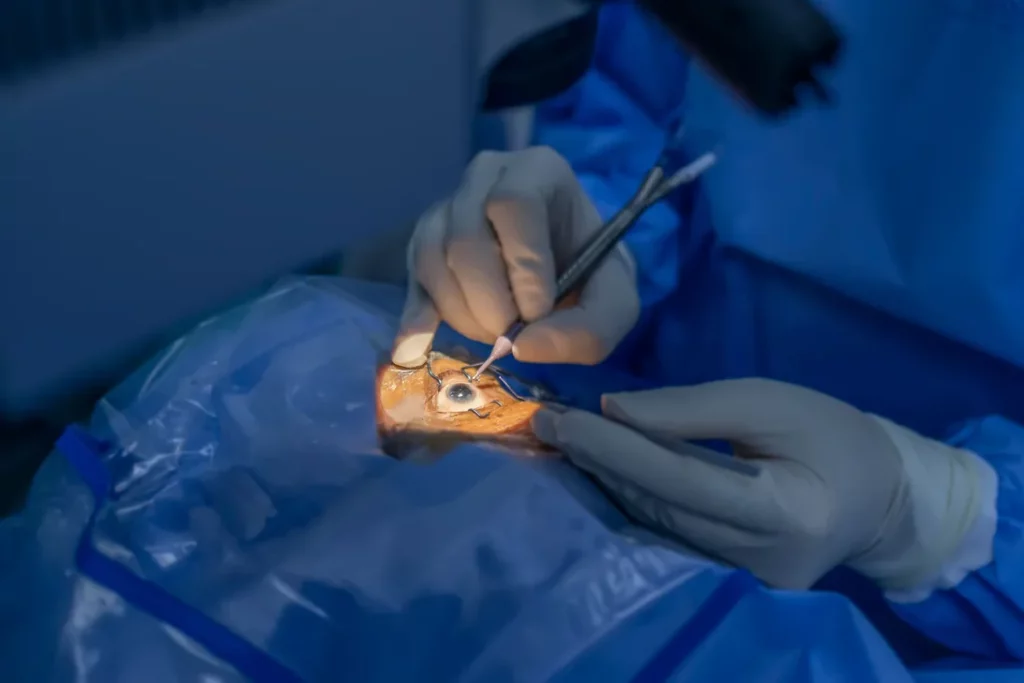
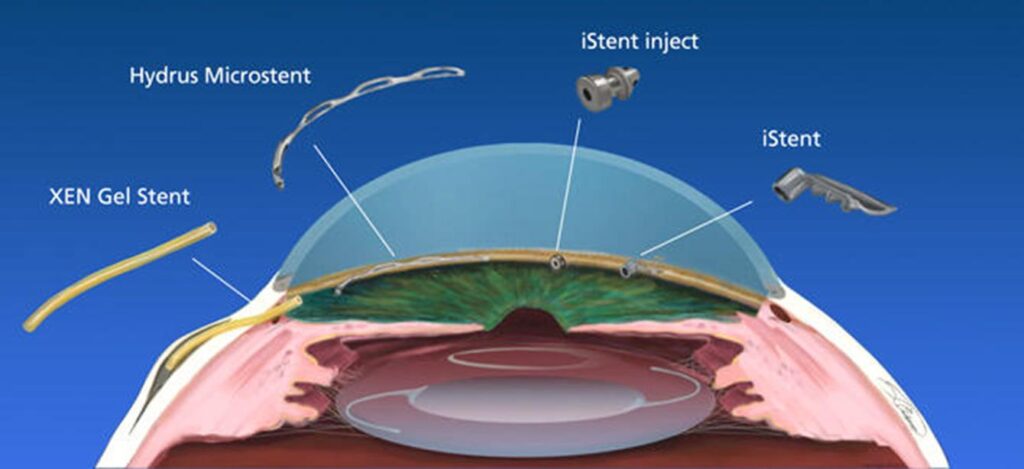
Surgical Procedures
In cases where medications are insufficient to manage intraocular pressure, surgical procedures may be necessary. Common operations include:
Laser therapy: to enhance fluid drainage.
Filtration surgery: creating a new drainage pathway for fluid.
Drainage implants: to facilitate fluid outflow if natural drainage is compromised.
Each treatment option must be evaluated with an eye care specialist to determine the most appropriate approach for individual cases. Surgical interventions can vary widely in complexity and recovery time, with some procedures being performed on an outpatient basis while others may require a hospital stay. Post-operative care is essential, as patients will need to attend follow-up appointments to ensure that the surgery was successful and that intraocular pressure is being effectively managed. Moreover, advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques have made it possible to reduce recovery times and improve outcomes, offering new hope for patients with more advanced glaucoma. To learn more about the surgical procedures click here.

Living with Glaucoma
Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with glaucoma requires some lifestyle adjustments to help manage the condition. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding activities that can increase eye pressure are essential steps. Gentle forms of exercise like walking or yoga can be beneficial, but patients should consult with their doctors before starting any new regimen. Incorporating activities that promote relaxation, such as tai chi or meditation, can also help reduce stress, which is known to impact overall health and well-being.
Moreover, patients should ensure to stay hydrated and consume antioxidant-rich foods that may support eye health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and flaxseeds, along with leafy greens and colorful fruits, can contribute to better eye function. It's also important to adhere strictly to prescribed medication regimens and maintain regular follow-up visits. Keeping a daily log of medication and symptoms can be a useful tool for both patients and their healthcare providers, facilitating more informed discussions during appointments.
Coping Mechanisms and Support
Adjusting to a glaucoma diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Patients may experience feelings of anxiety or depression due to the fear of potential vision loss. Connecting with support groups, whether in person or online, can provide comfort and reduce isolation. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can be incredibly therapeutic. Many organizations offer resources for coping strategies, including workshops and counseling services, which can help individuals process their emotions and find constructive ways to deal with their diagnosis.
Additionally, staying informed through educational resources and open discussions with eye care professionals can empower patients and help them navigate their journey with glaucoma more confidently. Attending seminars or webinars focused on glaucoma can provide valuable insights into the latest research and treatment options. Furthermore, involving family members in educational sessions can foster a supportive environment, allowing loved ones to better understand the condition and assist in daily management. This collective approach can enhance emotional resilience and create a stronger support network for those affected by glaucoma.
In conclusion, understanding glaucoma's symptoms, the importance of early detection, and the various treatment options available is crucial for patients. With proactive care, management strategies, and support networks, individuals living with glaucoma can maintain a good quality of life and preserve their vision for years to come.
Related : Eye Test for Glaucoma: Why It’s Essential for Early Detection